Role of standardization in safety
Introduction
There are multiple motives and incentives behind the standardization of operational processes, eliminating unnecessary costs is only one of them.
Unite-X puts into focus that standardized work makes processes not only effective but also safe.
This paper summarizes the insights of Unite-X experts, describing how standardization puts organizations on the rails towards Operational Safety Excellence. In this article, let’s look at the definition of a standard and how it supports safety and lean.
Image: The formation of safety culture in an organization
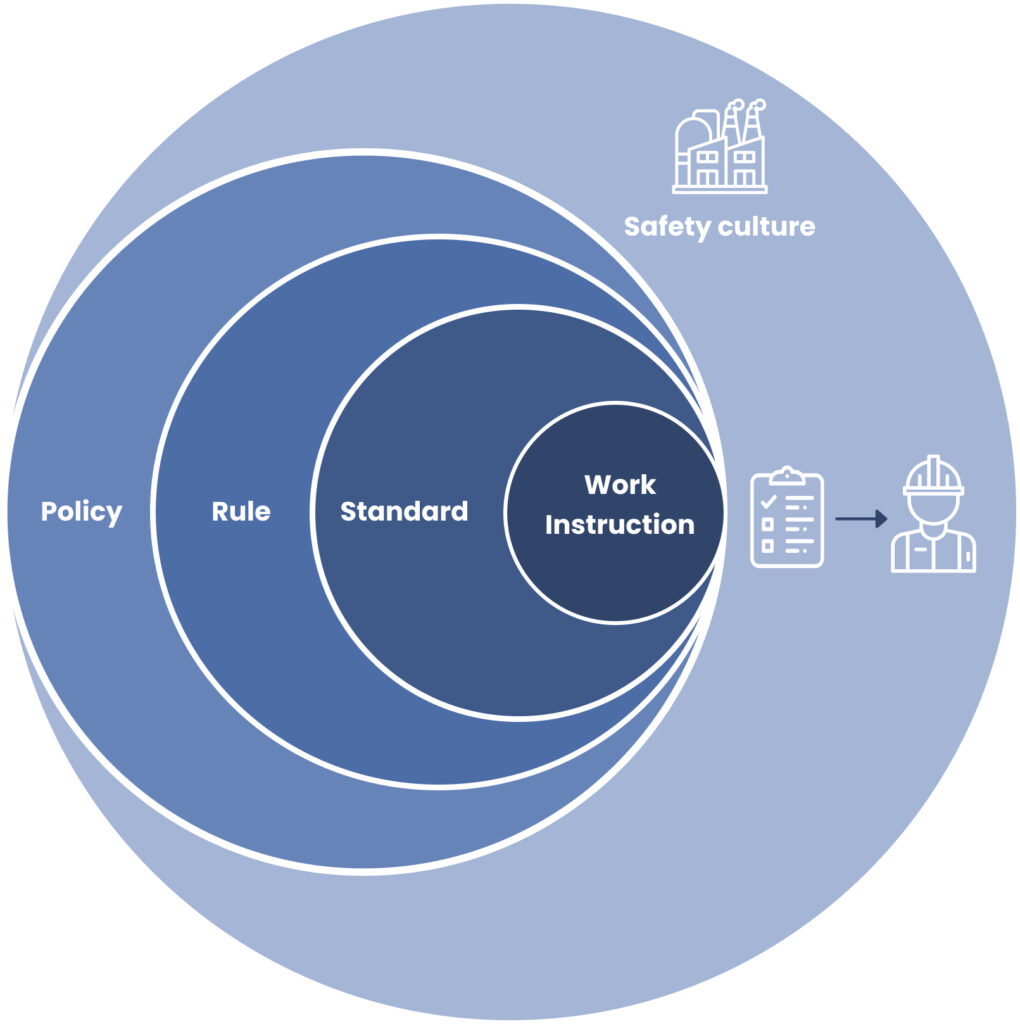
Safety
Creating and embracing a safety culture amongst sites of manufacturing organizations demands a high level of engagement from every person involved.
To achieve this, organizations need to develop a consistent safety culture and spread it across all the facilities globally, ensuring that this culture fits local specifics.
In its turn, working with standardized processes enables sharing experience, capture lessons learned, and cooperate for joined continuous improvement.
A standard
While standardization is the activity of making standards, there are numerous definitions of the term ‘standard’ used in the industry. In this paper, standardization is observed as a part of making production more lean and safe.
Thus in this paper, we rely on the definition that connects these two domains:
A standard is an approved specification of a limited set of solutions to an actual or potential matching problem, prepared for the benefits of the party or parties involved, balancing their needs, and prepared and intended to be used repeatedly or continuously for a certain period by a substantial number of parties for whom they are meant.
To decompose this definition from the lean perspective standard has the following characteristics:
-
-
- It is an approved specification
- It has a limited set of solutions
- It solves the actual or potential problem
- It is used repeatedly and continuously
- It is used for a certain period of time
- It is used by a substantial number of parties.
-
A standard must consider the users’ needs, and the usage of the standard must be beneficial.
Aside from that, standardized work is the focus of lean manufacturing. Thus concluding from the definition of standard, standardization is necessary for organizations that seek to elevate their safety to the next level.
Lean
Within the standardizing principles lies the idea that every abnormality in the process signals a potential error. At the same time, one of these principles is to avoid waste.
Additional safety measurements may result in additional procedures and when these procedures are not efficient, they form a process waste. Ironically, this triggers risks instead of preventing them. For example, long waiting times due to failed planning can result in rushed behavior in the maintenance process, not rarely at the expense of safety.
Standardizing safety procedures can prevent causing inefficient safety procedures to become waste. Based on the definition stated in the previous chapter and looking from the lean perspective, these are the benefits gained:
-
-
- To achieve maximal efficiency by uncovering and eliminating:
-
- Unnecessary workforce
- Inefficient costs
- Waiting time
-
- To achieve maximal efficiency by uncovering and eliminating:
-
-
-
- To achieve a higher level of safety by achieving
-
- Fewer incidents
- Less frustration
- Fewer possibilities for unnecessary risk-taking
-
- To achieve a higher level of safety by achieving
-
-
-
- To roll out the process across sites globally:
-
- To gain insights on how the corporate standard is applied locally
- To align in the understanding of process steps
- To develop a common perception of risk identification
-
- To roll out the process across sites globally:
-
-
-
- To set up flows of knowledge exchange amongst teams:
-
- To close the loop of lessons learned incorporation
- To review and adopt new developments
- To implement improvement ideas
-
- To set up flows of knowledge exchange amongst teams:
-
Going further down at the level of widely used safety operations, like Permit to Work or LoToTo, standardization brings:
-
-
- Necessary support for users in understanding and applying procedures
-
- Procedures translated into content and rules
- Rules translated into work instructions
- The first-time action performed right
-
- Improvement compatibility with other processes
- Possibility to monitor and review performance
-
- To benchmark and compare between sites
- To benchmark and compare across the industry
-
- Simplified communication with contractors
- Necessary support for users in understanding and applying procedures
-
As described above, there are numerous reasons to standardize safety procedures.
Conclusion
So, when done well, standardization decreases ambiguity and guesswork and increases employee morale.
When implemented successfully, standardization brings measurable improvements in important processes of an organization, such as planning, designing processes, quality of output, and compliance.
Unite-X considers standardization as an essential step towards Operational Safety Excellence.




